The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy made up of a supermassive black hole center, a central bar or bulge, and an outer spiral disk that is about three times the long axis of the inner bar. The Figure shows the bar and disk both simplified as rotating body pairs that radiate both scalar and vector gravity waves. The scalar gravity waves radiate outward from both bar and disk while the vector gravity waves couple disk to bar stars. The radiant vector gravity waves of the inner bar accelerate the outer disk stars and the radiant vector gravity wave of the disk decelerates the inner bar star rotations. The coupling of vector gravity then transfers angular momentum from slowing bar star rotations by accelerating disk star rotations.
Accelerating light leads to the simple axioms of discrete aether and quantum action. Matter action augments the more limited reality of continuous space, motion, and atomic time. With the quantum action of the Schrödinger equation and a single fundamental aether particle, two constants predict all action and all other physical constants. In the discovery of truth, there are only atoms and quantum action.
Search This Blog
Tuesday, December 20, 2022
Radiant Quantum Gravity of the Milky Way
Friday, November 11, 2022
Discrete Aether Quantum Gravity Radiation
For two orbiting bodies of very different masses like the
Sun and Mercury or the stars of a galaxy, the expression becomes
For two radiating and orbiting bodies like a binary star of
equal masses, there is an additional vector gravity term that is the ratio of
radiation and relative velocity.
Mercury has the largest eccentricity of any planet in its orbit with the Sun and the perihelion advance of Mercury has long validated Einstein’s relativity. Mercury’s perihelion advance is a result of gravity quadrupole radiation as Table 1 shows that decays its orbit and increases its velocity.
The emission of 5.2e-15 kg/s gravity quadrupole results in the Mercury orbit decay that is the perihelion advance. Since the same quadrupole emission occurs for discrete aether, the Mercury perihelion advance also validates discrete aether.
The Milky Way galaxy has a dipole luminosity of 4.3e19 kg/s, which is 1e10 x the Sun luminosity and due to its 2.5e11 stars. The gravity quadrupole Milky Way luminosity is much smaller at 1.3e15 kg/s than the dipole luminosity, but the much larger dipole luminosity also results in a quadrupole luminosity of 1.4e14 kg/s. This 13% increase in gravity wave emission decays all star orbits and therefore increases their orbital velocities just like the perihelion advance of Mercury.
The merger of two 6.0e31kg blackholes over 0.25 s results in quadrupole emissions of 3.0e29 kg/s at 1% of the total mass loss of the event. The onset of the inspiral occurs at r = 7.6e12 m, which is the point when the quadrupole radiation is just 1% of the total. There is also dipole emission from gravitation, but that emission is spread all over the universe.
Monday, October 10, 2022
Quantum Gravity of Discrete Aether
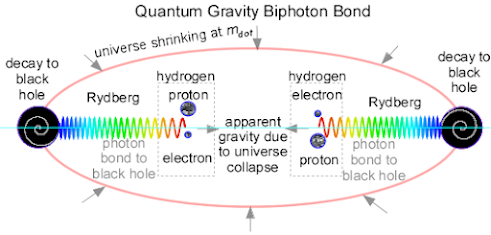
Quantum gravity is just a residual force of the quantum causal set, which exists outside of space and time. Instead of matter and action in space and time, space and time emerge from matter action of a causal set. Space as distance and time as relative quantum phases of the quantum photon exchange bonds emerge from neutral bodies like hydrogen atoms. Beyond a certain distance, about 70 nm for two hydrogens, quantum gravity is greater than the dispersion of quantum photon exchange. Quantum gravity between two hydrogen atoms is just the dispersion of quantum photon exchange of each atom with the rest of the universe.
Gravity relativity emerges from the fundamental equivalence of mass and energy for particles that exist in relativistic spacetime. To first order, the Lorentz invariance of the speed of light to velocity of a particle distorts space and time by the classic sqrt(1/(1 - v2/c2)). There are higher order terms that converge to the Einstein tensor as proportional to the energy-momentum tensor,
All of the complexity of general relativity reduces to this tensor equation and yet there is no accepted quantum gravity in spacetime. This is because each particle of matter introduces a singularity at r = 0 in spacetime that precludes a quantum electrodynamics exchange particle for gravity.
One consequence of GR is the black hole singularity that are widely accepted in general relativity but have no quantum meaning in QED. A black hole has mass and spin just like any other particle in the quantum causal set universe and black holes bond to the universe with photon exchange just like all matter particles. Thus, black holes are just another matter particle in a quantum causal set, which is about each matter body bonding to the rest of the universe with quantum photon exchange.
Thursday, July 21, 2022
Large Scale Structures in the Cosmic Microwave Background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) multipole analysis shows an angular scale consistent with a combination of 4.9% ordinary matter, 27% dark matter, and 68% dark energy expanding at 68 km/s.
However, this cosmology does not include quantum gravity at all and so there is no way to measure the absolute expansion rate of the universe. Although the small scale CMB structures are consistent with the cosmology without quantum gravity, there is an inconsistency in the large scale CMB structures of the universe as the figure shows.
A collapsing universe cosmology shows quantum gravity and a universe of ordinary matter that is only 1.1e-7 kg/kgAether, 8.7e-69 kg/aether, and 8.4e-61 kg.kgAether action collapsing at the rate of 77 km/s. The universe collapse quantum cosmology shows both a static gravity as well as a radiant vector gravity and the large scale CMB structures are consistent with radiant vector gravity.
Since the collapsing universe quantum gravity bonds with quadrupole biphoton exchange, there is now a vector component to gravity along with the Newtonian scalar gravity. Vector gravity couples the relative motions of stars much like magnetism couples the relative motions of charge. Since universe collapse is a matter decay that is the source of gravity, the matter decay of star radiation couples star motions as well as star convection.
Sunday, June 12, 2022
Scalar Static Matter and Vector Radiant Matter Gravity
Since matter-action gravitons are biphotons, which are entangled photons, there is not only scalar gravity due to static matter graviton shadows, but also a radiant vector gravity due to radiant matter. In other words, the radiation of stars entangles their motions with other stars and this entanglement results in radiant vector gravity.
Here is a diagram that shows scalar gravity shadows that results from the matter body bonds to the universe along with the radiant vector gravity that transfers momentum from inner to outer stars. Radiant vector gravity transfers momentum from stars inside the CofM to stars outside the CofM. This radiant momentum transfer is what keeps spiral galaxies rotating at constant velocity instead of at their Keplerian velocities.
The plot below shows the velocity profile of the Milky Way along with the observed Sun as opposed to the Keplerian Sun. The actual Sun velocity is about 29% greater than the Keplerian Sun velocity reported by Sofue et al, 251 vs. 194 km/s. The Keplerian gravity force at the Sun at 8.0 kpc is 8.4e14 kg m/s^2, which is consistent with a Sun velocity of 194 km/s as opposed to the actual Earth velocity of 251 km/s.Wednesday, June 1, 2022
Graviton Noise of Quantum Gravity
We live in an ocean of graviton noise and so it is graviton noise that is what makes things happen in our quantum reality. Entangled photons, biphotons, make up gravitons and are what bind each body to the universe of black holes. Black holes are the penultimate heat sink for all of our reality and what we see as gravity attraction is actually just the collapse of the universe matter and the interaction of photon geodesics.
The destiny of all black holes is then a single black hole that is the destiny of this cycle of the universe collapse. In other words, bodies do not really bond to each other with gravity. Instead each body bonds to the universe and we see gravity attraction as the universe collapse of photon geodesics.
The graviton noise of the universe photon geodesics is what makes all wavefunctions collapse and so graviton noise is also what makes reality real...
Wednesday, February 23, 2022
Discrete Aether Time Pulse
The discrete aether pulsed universe has a nice symmetry between its time pulse and the hydrogen time pulse defined by the Bohr time. The universe pulse is a 13.9 Byr sinc function of cosmic time with a Fourier transform that is dominated by the aether particle spectrum. The hydrogen pulse is a sinc function of cosmic time with a Fourier transform mass spectrum of the total universe mass that is 90% hydrogen mass.
Sunday, February 20, 2022
Discrete Aether Predictions
Star decay produces star matter waves that couple the motions of stars with a vector gravitization much like charge motions are coupled with vector magnetization. The two stars, Procyon and Cygni-61, are both 11.6 lyrs away from our sun, which couples their motions and affects the Sun’s convection with an 11.6 year period.
Sunspot activity went into a hiatus around 1680 as the plot shows, which is consistent with the Cygni-61A/Cygni-61B periapsis or closest approach at that time. Cygni-61 is a double star and so its double star orbit plays a role in the sunspot activity of our Sun. Thus, the 678 yr orbit of the Cygni-61A/B double star will reach apeosis again in the year 2358. The Procyon A/B double star has a 40.8 yr orbit and shows up as a 40.8 year shift in sunspot peak and intensity.
9) Since matter decay is equivalent to a force, discrete aether predicts that a matter decay of 83 MW/kg is equivalent to the 1.0 G force of earth’s gravity. The sun radiance is just 1.9e-4 W/kg and it would take a 1 kg U reactor pile 12,000 K to achieve 83 MW/kg. This is equivalent to a 1 kg U shell 22 m diameter radiating at 1,000 K, which is below the U melting point.
Tuesday, January 18, 2022
Single Photon Resonance as Fundamental Action
We only really see things that change and then we deduce how things are from how they change. It then seems reasonable that the universe is made up of not only things that change, but also things that are. Single photon resonances are the things that are and make up all change and single photon resonances occur between emitter precursors and absorber outcomes. Single photon spectra make up the fundamentally discrete nature of the universe with emitter and absorber chromophores.
A single photon resonance between emitter and absorber chromophores exists as a cosmic time packet that grows and then decays, which defines its time packet. Atomic time and space emerge from the quantum oscillations of that photon burst from the speed of light and its wavelength. The growth and decay of the photon packet define its location and direction and result in the Lorentzian spectrum that this example shows. The arrow of time emerges as the direction from primordial emitters to black hole absorber destiny outcomes.
The universe itself is then a spectrum of aether whose exponential decay defines not only a cosmic time, but also defines charge, gravity, and all forces along with the quantum oscillations from which atomic time and space emerge.